Associate Professor

 +86-0571-87951876
+86-0571-87951876
 xzxiao@zju.edu.cn
xzxiao@zju.edu.cn
 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027 China
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027 China
Dr. Xuezhang Xiao
School of Materials Science and Engineering
Zhejiang University
Hangzhou 310027 China
Tel: +86-0571-87951876
Fax:+86-0571-87951152
Email: xzxiao@zju.edu.cn
Dr. Xuezhang Xiao got the B.Sc. degree (2003) in Materials Physics from Central-South University, and Ph.D. degree (2008) in Materials Science from Zhejiang University, China, respectively. From July 2008 to June 2010, he joined the post-doctoral studies center of Chemical Engineering & Technology, Zhejiang University as a Postdoctoral Fellow. From December 2011 to May 2012, he visited the Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering, West Virginia University in USA as Research Scientist. From October 2013, he visited the School of Chemistry, University of Glasgow in UK as Academic Scholar. He became a faculty member at Zhejiang University as Lecturer in Sept. 2008 and as Associate Professor in Dec. 2010. He is carrying out four national research projects supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, National Basic Research Program and National Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China etc. He is a member of China Renewable Energy Society. He has published over 100 international refereed journal papers including Energy Storage Mater., J. Mater. Chem. A, Nanoscale, J. Alloys & Compd, J. Phys. Chem. C, and Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. enlisted in Science Citation Index (SCI), which h-index is 18.
His research interests are the basic researches and applications on renewable energy materials, including novel light metal and complex hydrides for hydrogen storage, nano/amorphous energy storage materials and devices for PEM fuel cell, Ni/MH batteries and Li/Na-ion battery.
ORCID ID https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4035-5044
Selected Publications List:
[1] Y.W. Zhang, X.Z. Xiao*, B.S. Luo, X. Huang, M.J. Liu, L.X. Chen, Synergistic Effect of LiBH4 and LiAIH4 Additives on Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of Unexpected High Capacity Magnesium Hydride, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 122 (2018) 2528-2538.
[2] W. Zhang, X.Z. Xiao*, Y.W. Zhang, J.P. Li, J.Y. Zhong, M. Li, X.L. Fan, C.T. Wang, L.X. Chen, In situ synthesized SnO2 nanorod/reduced graphene oxide low-dimensional structure for enhanced lithium storage, Nanotechnology, 29 (2018).
[3] X. Huang, X.Z. Xiao*, X.C. Wang, Z.D. Yao, C.T. Wang, X.L. Fan, L.X. Chen, Highly synergetic catalytic mechanism of Ni@g-C3N4 on the superior hydrogen storage performance of Li-Mg-B-H system, Energy Storage Materials 13 (2018) 199–206.
[4] Y.J. Liu, X.Z. Xiao*, X.L. Fan, M. Li, Y.W. Zhang, W. Zhang, L.X. Chen, GeP5/C composite as anode material for high power sodium-ion batteries with exceptional capacity, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 744 (2018) 15-22.
[5] Z.J. Liang, X.Z. Xiao*, X.Y. Yu, X. Huang, Y.Q. Jiang, X.L. Fan, L.X. Chen, Non-noble trimetallic Cu-Ni-Co nanoparticles supported on metal-organic frameworks as highly efficient catalysts for hydrolysis of ammonia borane, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 741 (2018) 501-508.
[6] Y.Q. Jiang, X.L. Fan, M. Chen, X.Z. Xiao*, Y.W. Zhang, C.T. Wang, L.X. Chen, AuPd Nanoparticles Anchored on Nitrogen-Decorated Carbon Nanosheets with Highly Efficient and Selective Catalysis for the Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 122 (2018) 4792-4801.
[7] J.G. Zheng, X.Z. Xiao*, L.T. Zhang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, Facile synthesis of bowl-like 3D Mg(BH4)2-NaBH4-fluorographene composite with unexpected superior dehydrogenation performances, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5 (2017) 9723-9732.
[8] J.G. Zheng, X.Z. Xiao*, L.T. Zhang, Y. He, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, Study on the dehydrogenation properties and reversibility of Mg(BH4)(2)-AlH3 composite under moderate conditions, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 42 (2017) 8050-8056.
[9] W. Zhang, M. Li, X.Z. Xiao*, X. Huang, Y.Q. Jiang, X.L. Fan, L.X. Chen, In situ synthesis of ultrasmall SnO2 quantum dots on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide composite as high performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 727 (2017) 1-7.
[10] L.T. Zhang, J.G. Zheng, X.Z. Xiao*, X.C. Wang, X. Huang, M.J. Liu, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, A new strategy to remarkably improve the low-temperature reversible hydrogen desorption performances of LiBH4 by compositing with fluorographene, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 42 (2017) 20046-20055.
[11] L.T. Zhang, J.G. Zheng, X.Z. Xiao*, X.L. Fan, X. Huang, X.L. Yang, L.X. Chen, Enhanced hydrogen storage properties of a dualcation (Li+, Mg2+) borohydride and its dehydrogenation mechanism, Rsc Advances, 7 (2017) 36852-36859.
[12] X. Xiao, T. Qin, Y. Jiang, F. Jiang, M. Li, X. Fan, S. Li, H. Ge, Q. Wang, L. Chen, Significantly enhanced hydrogen desorption properties of Mg(AlH4)(2) nanoparticles synthesized using solvent free strategy, Progress In Natural Science-Materials International, 27 (2017) 112-120.
[13] C.C. Weng, X.Z. Xiao*, X. Huang, F.L. Jiang, Z.D. Yao, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, Effect of Mn substitution for Co on the structural, kinetic, and thermodynamic characteristics of ZrCo1-xMnx (x=0-0.1) alloys for tritium storage, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 42 (2017) 28498-28506.
[14] M. Li, X.Z. Xiao*, X.L. Fan, X. Huang, Y.J. Liu, L.X. Chen, Carbon coated sodium-titanate nanotube as an advanced intercalation anode material for sodium-ion batteries, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 712 (2017) 365-372.
[15] M. Li, X. Xiao*, Y. Liu, W. Zhang, Y. Zhang, L. Chen, Ternary perovskite cobalt titanate/graphene composite material as long-term cyclic anode for lithium-ion battery, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 700 (2017) 54-60.
[16] X. Huang, X. Xiao*, W. Zhang, X. Fan, L. Zhang, C. Cheng, S. Li, H. Ge, Q. Wang, L. Chen, Transition metal (Co, Ni) nanoparticles wrapped with carbon and their superior catalytic activities for the reversible hydrogen storage of magnesium hydride, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 19 (2017) 4019-4029.
[17] B. Zhai, X. Xiao*, W. Lin, X. Huang, X. Fan, S. Li, H. Ge, Q. Wang, L. Chen, Enhanced hydrogen desorption properties of LiBH4-Ca(BH4)2 by a synergetic effect of nanoconfinement and catalysis, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 41 (2016) 17462-17470.
[18] C.C. Xu, X.Z. Xiao*, J. Shao, L.X. Liu, T. Qin, L.X. Chen, Effects of Ti-based additives on Mg2FeH6 dehydrogenation properties, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 26 (2016) 791-798.
[19] X.Z. Xiao, Z. Liu, S. Saremi-Yarahmadi, D.H. Gregory, Facile preparation of beta-/gamma-MgH2 nanocomposites under mild conditions and pathways to rapid dehydrogenation, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 18 (2016) 10492-10498.
[20] X. Huang, X.Z. Xiao*, J. Shao, B. Zhai, X.L. Fan, C.J. Cheng, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Building robust architectures of carbon-wrapped transition metal nanoparticles for high catalytic enhancement of the 2LiBH(4)-MgH2 system for hydrogen storage cycling performance, Nanoscale, 8 (2016) 14898-14908.
[21] L.T. Zhang, J.G. Zheng, L.X. Chen, X.Z. Xiao*, T. Qin, Y.Q. Jiang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Remarkable enhancement in dehydrogenation properties of Mg(BH4)(2) modified by the synergetic effect of fluorographite and LiBH4, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 40 (2015) 14163-14172.
[22] L.T. Zhang, X.Z. Xiao*, C.C. Xu, J.G. Zheng, X.L. Fan, J. Shao, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Remarkably Improved Hydrogen Storage Performance of MgH2 Catalyzed by Multivalence NbHx Nanoparticles, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 8554-8562.
[23] X.Z. Xiao, C.C. Xu, J. Shao, L.T. Zhang, T. Qin, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Remarkable hydrogen desorption properties and mechanisms of the Mg2FeH6@MgH2 core-shell nanostructure, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3 (2015) 5517-5524.
[24] L.T. Zhang, X.Z. Xiao*, X.L. Fan, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Fast hydrogen release under moderate conditions from NaBH4 destabilized by fluorographite, Rsc Advances, 4 (2014) 2550-2556.
[25] L.T. Zhang, L.X. Chen, X.Z. Xiao*, Z.W. Chen, S.K. Wang, X.L. Fan, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Superior dehydrogenation performance of nanoscale lithium borohydride modified with fluorographite, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 39 (2014) 896-904.
[26] X.Z. Xiao, S.K. Wang, G.P. Tu, L.T. Zhang, X.L. Fan, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Enhanced reversible hydrogen storage performance of NbCl5 doped 2LiH-MgB2 composite, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 39 (2014) 2132-2141.
[27] X.Z. Xiao, S.K. Wang, X.L. Fan, C.C. Xu, J. Sun, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Improved de/hydrogenation properties and favorable reaction mechanism of CeH2 + KH co-doped sodium aluminum hydride, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 39 (2014) 6577-6587.
[28] X.Z. Xiao, L.T. Zhang, X.L. Fan, L.Y. Han, J. Shao, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Synergetic Effect of in Situ Formed Nano NbH and LiH1-xFx for Improving Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties of the Li-Mg-B-H System, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 12019-12025.
[29] X.Z. Xiao, J. Shao, L.X. Chen, H.Q. Kou, X.L. Fan, S.S. Deng, L.T. Zhang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Effects of NbF5 addition on the de/rehydrogenation properties of 2LiBH(4)/MgH2 hydrogen storage system, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 37 (2012) 13147-13154.
[30] H.Q. Kou, X.Z. Xiao*, J.X. Li, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Effects of fluoride additives on dehydrogenation behaviors of 2LiBH A Novel Li-Ca-B-H Complex Borohydrid (4)+MgH2 system, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 37 (2012) 1021-1026.
[31] X.Z. Xiao, K.R. Yu, X.L. Fan, Z. Wu, X.H. Wang, C.P. Chen, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Synthesis and hydriding/dehydriding properties of nanosized sodium alanates prepared by reactive ball-milling, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 36 (2011) 539-548.
[32] X.Z. Xiao, C.X. Li, L.X. Chen, X.L. Fan, H.Q. Kou, Q.D. Wang, Synthesis and dehydrogenation of CeAl4-doped calcium alanate, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 509 (2011) S743-S746.
[33] K. Jiang, X.Z. Xiao*, S.S. Deng, M. Zhang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, A Novel Li-Ca-B-H Complex Borohydride: Its Synthesis and Hydrogen Storage Properties, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (2011) 19986-19993.
[34] Z.M. Hang, L.X. Chen, X.Z. Xiao*, S.Q. Li, C.P. Chen, Y.Q. Lei, Q.D. Wang, The effect of Cr content on the structural and hydrogen storage characteristics of Ti10V80-xFe6Zr4Crx (x=0-14) alloys, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 493 (2010) 396-400.
[35] X.Z. Xiao, G.C. Liu, S.K. Peng, K.R. Yu, S.Q. Li, C.P. Chen, L.X. Chen, Microstructure and hydrogen storage characteristics of nanocrystalline Mg plus x wt% LaMg2Ni (x=0-30) composites, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 35 (2010) 2786-2790.
[36] X.Z. Xiao, X.L. Fan, K.R. Yu, S.Q. Li, C.P. Chen, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Catalytic Mechanism of New TiC-Doped Sodium Alanate for Hydrogen Storage, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 20745-20751.
[37] X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, Z.M. Hang, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, C.P. Chen, Y.Q. Lei, Q.D. Wang, Microstructures and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of novel Mg-Al-Ni amorphous composites, Electrochemistry Communications, 11 (2009) 515-518.
[38] X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.L. Fan, X.H. Wang, C.P. Chen, Y.Q. Lei, Q.D. Wang, Direct synthesis of nanocrystalline NaAlH4 complex hydride for hydrogen storage, Applied Physics Letters, 94 (2009).
[39] X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, C.P. Chen, Q.D. Wang, Reversible hydrogen storage properties and favorable co-doping mechanism of the metallic Ti and Zr co-doped sodium aluminum hydride, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 33 (2008) 64-73.
[40] X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, Q.D. Wang, C.P. Chen, The hydrogen storage properties and microstructure of Ti-doped sodium aluminum hydride prepared by ball-milling, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 32 (2007) 2475-2479.
[41] X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, Q.D. Wang, C.P. Chen, Influence of temperature and hydrogen pressure on the hydriding/dehydriding behavior of Ti-doped sodium aluminum hydride, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 32 (2007) 3954-3958.
[42] X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, Z.M. Hang, C.P. Chen, Q.D. Wang, Dehydriding properties of Ti or/and Zr-doped sodium aluminum hydride prepared by ball-milling, Physica Scripta, T129 (2007) 95-98.
[43] X.Z. Xiao, X.H. Wang, L.H. Gao, L. Wang, C.P. Chen, Electrochemical properties of amorphous Mg-Fe alloys mixed with Ni prepared by ball-milling, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 413 (2006) 312-318.
[44] G.P. Tu, X.Z. Xiao, Y.Q. Jiang, T. Qin, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Composite cooperative enhancement on the hydrogen desorption kinetics of LiBH4 by co-doping with NbCl5 and hexagonal BN, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 40 (2015) 10527-10535.
[45] J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, X.L. Fan, X. Huang, B. Zhai, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Enhanced hydrogen storage capacity and reversibility of LiBH4 nanoconfined in the densified zeolite-templated carbon with high mechanical stability, Nano Energy, 15 (2015) 244-255.
[46] L.X. Liu, L.X. Chen, X.Z. Xiao, C.C. Xu, J. Sun, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.J. Jiang, Influence of annealing treatment on the microstructure and hydrogen storage performance of Ti1.02Cr1.1Mn0.3Fe0.6 alloy for hybrid hydrogen storage application, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 636 (2015) 117-123.
[47] J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, X.L. Fan, L.T. Zhang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Low-Temperature Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties of LiBH4: A Synergetic Effect of Nanoconfinement and Nanocatalysis, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 11252-11260.
[48] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, J. Shao, L.T. Zhang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Superior Catalytic Effects of Transition Metal Boride Nanoparticles on the Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties of Li-Mg-B-H System, Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 31 (2014) 195-200.
[49] X.L. Fan, J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, C.S. Wang, In situ synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles encapsulated in micro/mesoporous carbon foam as a high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2 (2014) 18367-18374.
[50] X.L. Fan, J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, SnLi4.4 nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon matrix as high performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries, Nano Energy, 9 (2014) 196-203.
[51] X.L. Fan, J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Carbon encapsulated 3D hierarchical Fe3O4 spheres as advanced anode materials with long cycle lifetimes for lithium-ion batteries, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2 (2014) 14641-14648.
[52] Z.W. Chen, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.L. Fan, L.X. Liu, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Influence of Ti super-stoichiometry on the hydrogen storage properties of Ti1+xCr1.2Mn0.2Fe0.6 (x=0-0.1) alloys for hybrid hydrogen storage application, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 585 (2014) 307-311.
[53] J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.L. Fan, L.Y. Han, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Enhanced hydriding-dehydriding performance of a 2LiH-MgB2 composite by the catalytic effects of Ni-B nanoparticles, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1 (2013) 10184-10192.
[54] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, J. Shao, L.T. Zhang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Size effect on hydrogen storage properties of NaAlH4 confined in uniform porous carbons, Nano Energy, 2 (2013) 995-1003.
[55] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, L.T. Zhang, J. Shao, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Significantly improved hydrogen storage properties of NaAlH4 catalyzed by Ce-based nanoparticles, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1 (2013) 9752-9759.
[56] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, High catalytic efficiency of amorphous TiB2 and NbB2 nanoparticles for hydrogen storage using the 2LiBH(4)-MgH2 system, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1 (2013) 11368-11375.
[57] Z.W. Chen, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.L. Fan, L.X. Liu, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Development of Ti-Cr-Mn-Fe based alloys with high hydrogen desorption pressures for hybrid hydrogen storage vessel application, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 38 (2013) 12803-12810.
[58] J. Shao, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, X.L. Fan, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Enhanced hydriding-dehydriding performance of 2LiBH(4)-MgH2 composite by the catalytic effects of transition metal chlorides, Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22 (2012) 20764-20772.
[60] Y. Li, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, L.Y. Han, J. Shao, X.L. Fan, S.Q. Li, Q.D. Wang, Effects of Fluoride Additives on the Hydrogen Storage Performance of 2LiBH(4)-Li3AlH6 Destabilized System, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 22226-22230.
[61] C.X. Li, X.Z. Xiao, P.Q. Ge, J.W. Xue, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, L.X. Chen, Investigation on synthesis, structure and catalytic modification of Ca(AlH4)(2) complex hydride, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 37 (2012) 936-941.
[62] K. Jiang, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, L.Y. Han, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, A comparative study of the hydrogen storage properties of LiBH4 doping with CaHCl and CaH2, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 539 (2012) 103-107.
[63] Z.M. Hang, X.Z. Xiao, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, C.P. Chen, L.X. Chen, Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti10V77Cr6Fe6Zr alloy, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 529 (2012) 128-133.
[64] S.S. Deng, X.Z. Xiao, L.Y. Han, Y. Li, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, L.X. Chen, Hydrogen storage performance of 5LiBH(4)+Mg2FeH6 composite system, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 37 (2012) 6733-6740.
[65] C.X. Li, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, K. Jiang, S.Q. Li, Q.D. Wang, Synthesis of calcium alanate and its dehydriding performance enhanced by FeF3 doping, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 509 (2011) 590-595.
[66] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, S.Q. Li, Q.D. Wang, Investigation on the nature of active species in the CeCl3-doped sodium alanate system, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 509 (2011) S750-S753.
[67] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Enhanced Hydriding-Dehydriding Performance of CeAl2-Doped NaAlH4 and the Evolvement of Ce-Containing Species in the Cycling, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (2011) 2537-2543.
[68] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, L.Y. Han, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Hydriding-dehydriding kinetics and the microstructure of La- and Sm-doped NaAlH4 prepared via direct synthesis method, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 36 (2011) 10861-10869.
[69] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, L.Y. Han, S.Q. Li, H.W. Ge, Q.D. Wang, Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Modeling Investigation on the Dehydrogenation of CeAl4-Doped NaAlH4 Hydrogen Storage Material, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (2011) 22680-22687.
[70] Z.M. Hang, X.Z. Xiao, K.R. Yu, S.Q. Li, C.P. Chen, L.X. Chen, Influence of Fe content on the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti16Zr5Cr22V57-xFex (x=2-8) alloys, Int J Hydrogen Energ, 35 (2010) 8143-8148.
[71] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, J.C. Hou, Z. Zhang, Y.B. Liu, Z. Wu, C.P. Chen, Q.D. Wang, L. Chen, Reversible hydrogen storage behaviors and microstructure of TiC-doped sodium aluminum hydride, Journal of Materials Science, 44 (2009) 4700-4704.
[72] X.L. Fan, X.Z. Xiao, L.X. Chen, K.R. Yu, Z. Wu, S.Q. Li, Q.D. Wang, Active species of CeAl4 in the CeCl3-doped sodium aluminium hydride and its enhancement on reversible hydrogen storage performance, Chemical Communications, (2009) 6857-6859.
Research Areas
Courses
This course is an introduction of the basic principles of materials chemistry and their applications in the field of materials science and engineering. It starts with three basic concepts: temperature, energy and entropy. Topics involved are quantum chemistry, statistical thermodynamics, classical thermodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, surface chemistry and colloidal chemistry.
Publications
ORCID ID https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4035-5044
Select SCI Papers:
[141] X. Wang, X. Xiao*, J. Zheng, Z. Yao, M. Zhang, X. Huang, L. Chen, Insights into magnesium borohydride dehydrogenation mechanism from its partial reversibility under moderate conditions, Materials Today Energy, 2020; 18: 100552.
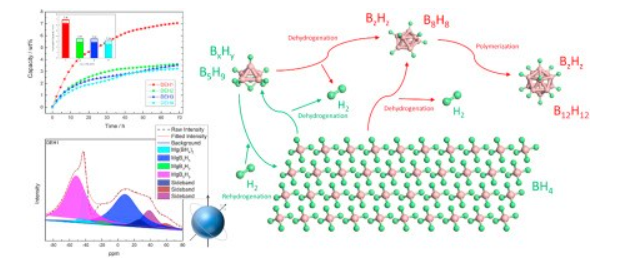
[140] H. Cheng, J. Zheng, X. Xiao*, Z. Liu, X. Ren, X. Wang, S. Li, L. Chen, Ultra-fast dehydrogenation behavior at low temperature of LiAlH4 modified by fluorographite, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020; 45: 28123-28133.
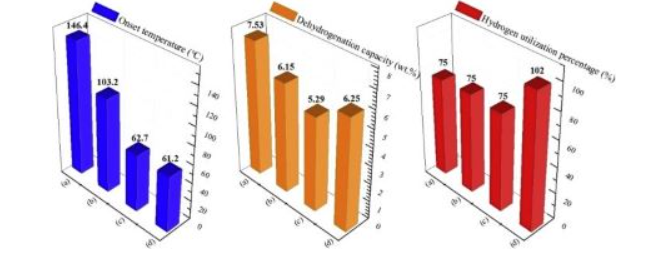
[139] Z. Yao, Z. Liang, X. Xiao*, X. Huang, J. Liu, X. Wang, J. Zheng, H. Kou, W. Luo, C. Chen, L. Chen, An impact of hydrogenation phase transformation mechanism on the cyclic stabilizing behavior of Zr0.8Ti0.2Co alloy for hydrogen isotope handling, Materials Today Energy, 2020; 18: 100554.
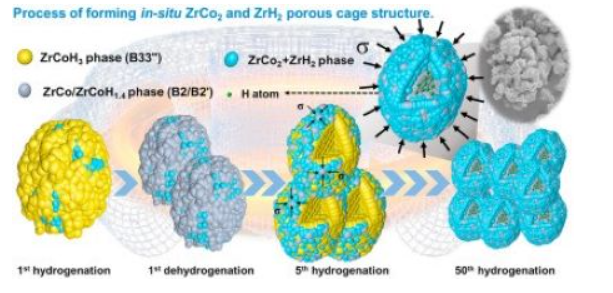
[138] X. Huang, X. Xiao*, Y. He, Z. Yao, X. Ye, H. Kou, C. Chen, T. Huang, X. Fan and L. Chen, Probing an intermediate state by X-ray absorption near-edge structure in nickel-doped 2LiBH4–MgH2 reactive hydride composite at moderate temperature, Materials Today Nano, 2020; 12: 100090.
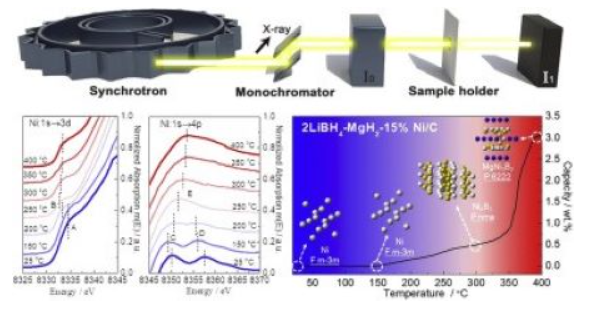
[137] Z. Liang, Z. Yao, X. Xiao*, H. Kou, W. Luo, C. Chen and L. Chen, The functioning mechanism of Al valid substitution for Co in improving the cycling performance of Zr–Co–Al based hydrogen isotope storage alloys, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020; 848: 156618.
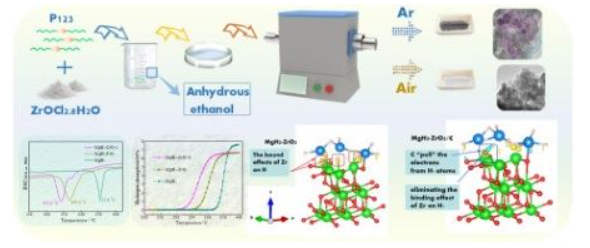
[136] M. Chen, X. Xiao*, X. Wang, Y. Lu, M. Zhang, J. Zheng, L. Chen, Self-templated carbon enhancing catalytic effect of ZrO2 nanoparticles on the excellent dehydrogenation kinetics of MgH2, Carbon, 2020; 166: 46-55.
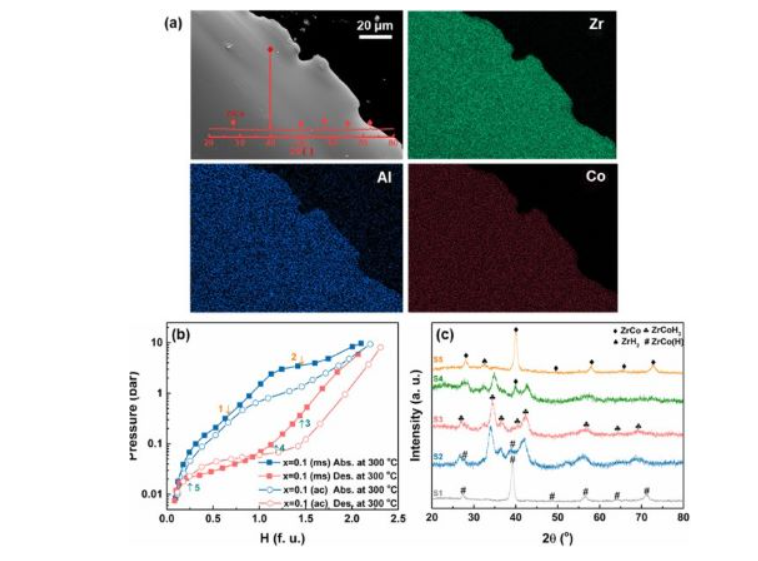
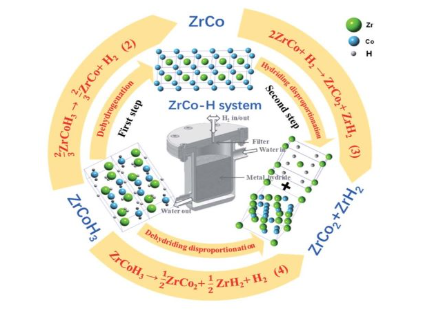
[135] Z. Yao, X. Xiao*, Z. Liang, X. Huang, H. Kou, W. Luo, C. Chen, L. Chen, An in-depth study on the thermodynamics and kinetics of disproportionation behavior in ZrCo–H systems, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020; 8: 9322-9330.
[134] W. Lin, X. Xiao*, X. Wang, J.-W. Wong, Z. Yao, M. Chen, J. Zheng, Z. Hu, L. Chen, Extreme high reversible capacity with over 8.0 wt% and excellent hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 combined with LiBH4 and Li3AlH6, Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020; 50: 296-306.
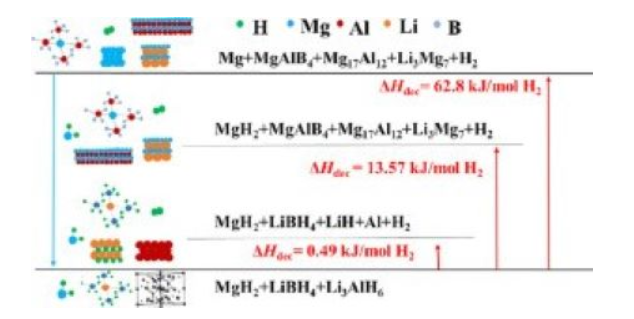
[133] M. Chen, X. Xiao*, M. Zhang, J. Mao, J. Zheng, M. Liu, X. Wang, L. Chen, Insights into 2D graphene-like TiO2 (B) nanosheets as highly efficient catalyst for improved low-temperature hydrogen storage properties of MgH2, Materials Today Energy, 2020; 16: 100411.
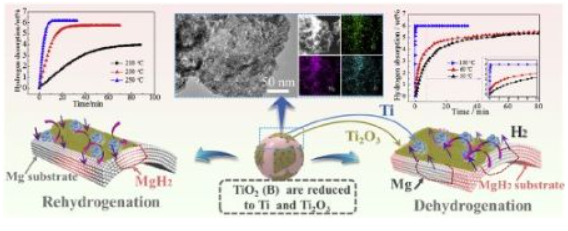
[132] J. Zheng, H. Cheng, X. Wang, M. Chen, X. Xiao*, L. Chen, LiAlH4 as a “Microlighter” on the Fluorographite Surface Triggering the Dehydrogenation of Mg(BH4)2: Toward More than 7 wt % Hydrogen Release below 70 °C, ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020; 3(3): 3033-3041.
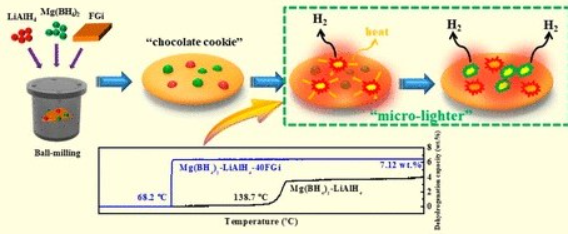
[131] J. Zhong, X. Xiao*, Z. Wu, N. Zhang, R. Jiang, X. Fan, L. Chen, Enhancing the reversibility of SnCoS4 microflower for sodium-ion battery anode material, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020; 825: 154104.
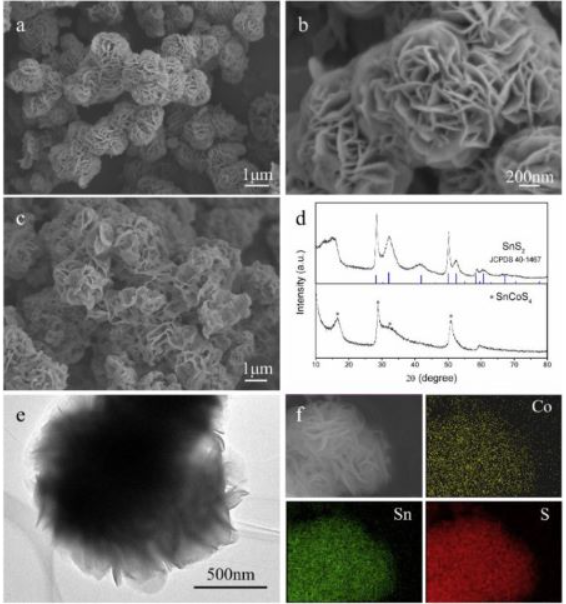
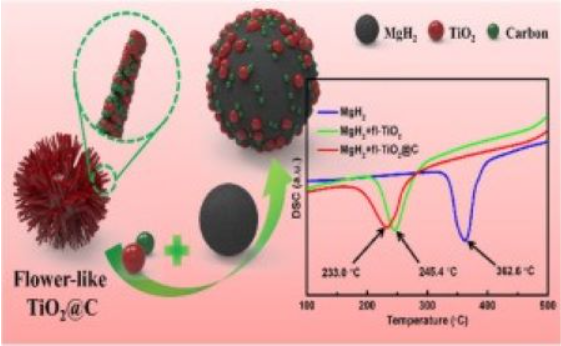
[130] M. Zhang, X. Xiao*, B. Luo, M. Liu, M. Chen, L. Chen. Superior de/hydrogenation performances of MgH2 catalyzed by 3D flower-like TiO2@C nanostructures, Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020; 46: 191-198.
[129] X. Wang, X. Xiao*, J. Zheng, X. Huang, M. Chen, L. Chen. In-situ synthesis of amorphous Mg(BH4)2 and chloride composite modified by NbF5 for superior reversible hydrogen storage properties. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020; 45: 2044-2053.
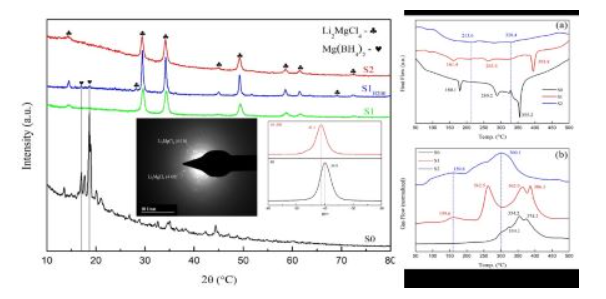
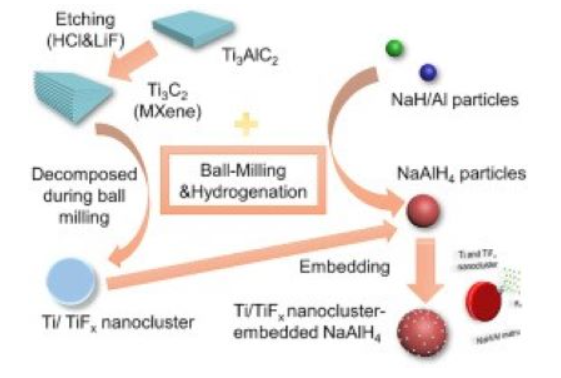
[128] R. Jiang, X. Xiao*, J. Zheng, M. Chen, L. Chen. Remarkable hydrogen absorption/desorption behaviors and mechanism of sodium alanates in-situ doped with Ti-based 2D MXene, Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020; 242: 122529.
[127] J. Y. Zhong, X. Z. Xiao*, Y. W. Zhang et al. Rational design of Sn-Sb-S composite with yolk-shell hydrangea-like structure as advanced anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019; 793: 620-626.
[126] J. G. Zheng, H. Cheng, X. Z. Xiao*, M. Chen, L. X. Chen. Enhanced low temperature hydrogen desorption properties and mechanism of Mg(BH4)2 composited with 2D MXene. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 24292-24300.
[125] Y. Zhang, X. Xiao*, W. Zhang et al. Facile formation of NiCo2O4 yolk-shell spheres for highly reversible sodium storage. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019; 800: 125-133.
[124] M. Zhang, X. Z. Xiao*, X. W. Wang et al. Excellent catalysis of TiO2 nanosheets with high-surface-energy {001} facets on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Nanoscale 2019; 11: 7465-7473.
[123] M. Zhang, X. Xiao*, J. Mao et al. Synergistic catalysis in monodispersed transition metal oxide nanoparticles anchored on amorphous carbon for excellent low-temperature dehydrogenation of magnesium hydride. Materials Today Energy 2019; 12: 146-154.
[122] Z. D. Yao, X. Z. Xiao*, Z. Q. Liang et al. Improvement on the kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of Zr1-xNbxCo (x=0-0.2) alloys for hydrogen isotope storage and delivery. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019; 784: 1062-1070.
[121] Z. D. Yao, X. Z. Xiao*, Z. Q. Liang et al. Study on the modification of Zr-Mn-V based alloys for hydrogen isotopes storage and delivery. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019; 797: 185-193.
[120] M. J. Liu, S. C. Zhao, X. Z. Xiao* et al. Novel 1D carbon nanotubes uniformly wrapped nanoscale MgH2 for efficient hydrogen storage cycling performances with extreme high gravimetric and volumetric capacities. Nano Energy 2019; 61: 540-549.
[119] M. J. Liu, X. Z. Xiao*, S. C. Zhao et al. ZIF-67 derived Co@CNTs nanoparticles: Remarkably improved hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 and synergetic catalysis mechanism. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 1059-1069.
[118] M. J. Liu, X. Z. Xiao*, S. C. Zhao et al. Facile synthesis of Co/Pd supported by few-walled carbon nanotubes as an efficient bidirectional catalyst for improving the low temperature hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2019; 7: 5277-5287.
[117] Z. Q. Liang, X. Z. Xiao*, Z. D. Yao et al. A new strategy for remarkably improving anti-disproportionation performance and cycling stabilities of ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloys by Cu substitution and controlling cutoff desorption pressure. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 28242-28251.
[116] X. Huang, X. Z. Xiao*, X. C. Wang et al. In-situ formation of ultrafine MgNi3B2 and TiB2 nanoparticles: Heterogeneous nucleating and grain coarsening retardant agents for magnesium borate in Li-Mg-B-H reactive hydride composite. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 27529-27541.
[115] Z. C. Hu, H. Y. Qin, X. Z. Xiao* et al. Excellent Catalysis of Various TiO2 Dopants with Na0.46TiO2 in Situ Formed on the Enhanced Dehydrogenation Properties of NaMgH3. Journal Of Physical Chemistry C 2019; 123: 22832-22841.
[114] X. L. Fan, X. Ji, L. Chen, J. Chen, T. Deng, F. D. Han, J. Yue, N. Piao, R. X. Wang, X. Q. Zhou, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, and C. S. Wang. All-temperature batteries enabled by fluorinated electrolytes with non-polar solvents. Nature Energy 2019; 4: 882-890.
[113] Z. Dong, F. Y. Li, Q. He, X. Z. Xiao* et al. PdCoNi nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets for room temperature dehydrogenation of formic acid. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 11675-11683.
[112] M. Chen, X. Z. Xiao*, M. Zhang et al. Excellent synergistic catalytic mechanism of in-situ formed nanosized Mg2Ni and multiple valence titanium for improved hydrogen desorption properties of magnesium hydride. International Journal Of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 1750-1759.
[111] M. Chen, X. Z. Xiao*, M. Zhang et al. Highly dispersed metal nanoparticles on TiO2 acted as nano redox reactor and its synergistic catalysis on the hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2019; 44: 15100-15109.
[110] J. G. Zheng, X. Z. Xiao*, Y. He et al. Enhanced reversible hydrogen desorption properties and mechanism of Mg(BH4)2-AlH3-LiH composite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2018; 762: 548-554.
[109] Y. W. Zhang, X. Z. Xiao*, B. S. Luo, X. Huang, M. J. Liu, L. X. Chen. Synergistic Effect of LiBH4 and LiAIH4 Additives on Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of Unexpected High Capacity Magnesium Hydride. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018; 122: 2528-2538.
[108] W. Zhang, X. Z. Xiao*, Y. W. Zhang et al. In situ synthesized SnO2 nanorod/reduced graphene oxide low-dimensional structure for enhanced lithium storage. Nanotechnology 2018; 29.
[107] Z. D. Yao, L. X. Liu, X. Z. Xiao*, C. T. Wang, L. J. Jiang, L. X. Chen. Effect of rare earth doping on the hydrogen storage performance of Ti1.02Cr1.1Mn0.3Fe0.6 alloy for hybrid hydrogen storage application. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2018; 731: 524-530.
[106] Y. J. Liu, X. Z. Xiao*, X. L. Fan et al. GeP5/C composite as anode material for high power sodium-ion batteries with exceptional capacity. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2018; 744: 15-22.
[105] Z. J. Liang, X. Z. Xiao*, X. Y. Yu et al. Non-noble trimetallic Cu-Ni-Co nanoparticles supported on metal-organic frameworks as highly efficient catalysts for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2018; 741: 501-508.
[104] Y. Q. Jiang, X. L. Fan, M. Chen, X. Z. Xiao* et al. AuPd Nanoparticles Anchored on Nitrogen-Decorated Carbon Nanosheets with Highly Efficient and Selective Catalysis for the Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018; 122: 4792-4801.
[103] Y. Q. Jiang, M. Chen, Y. F. Yang, X. L. Zhang, X. Z. Xiao* et al. Facile synthesis of AuPd nanoparticles anchored on TiO2 nanosheets for efficient dehydrogenation of formic acid. Nanotechnology 2018; 29: 8.
[102] X. Huang, X. Z. Xiao*, X. C. Wang et al. Highly synergetic catalytic mechanism of Ni@g-C3N4 on the superior hydrogen storage performance of Li-Mg-B-H system. Energy Storage Materials 2018; 13: 199-206.
[101] X. Huang, X. Z. Xiao*, X. C. Wang et al. Synergistic Catalytic Activity of Porous Rod-like TMTiO3 (TM = Ni and Co) for Reversible Hydrogen Storage of Magnesium Hydride. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018; 122: 27973-27982.
[100] C. J. Cheng, M. Chen, X. Z. Xiao*, X. Huang, J. G. Zheng, L. X. Chen. Superior Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties and Mechanism of LiBH4-MgH2-Al Doped with NbF5 Additive. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018; 122: 7613-7620.
[99] J. G. Zheng, X. Z. Xiao, L. T. Zhang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, L. X. Chen. Facile synthesis of bowl-like 3D Mg(BH4)2-NaBH4-fluorographene composite with unexpected superior dehydrogenation performances. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2017; 5: 9723-9732.
[98] J. G. Zheng, X. Z. Xiao, L. T. Zhang et al. Study on the dehydrogenation properties and reversibility of Mg(BH4)2-AlH3 composite under moderate conditions. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017; 42: 8050-8056.
[97] W. Zhang, M. Li, X. Z. Xiao et al. In situ synthesis of ultrasmall SnO2 quantum dots on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide composite as high performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Alloys And Compounds 2017; 727: 1-7.
[96] L. T. Zhang, J. G. Zheng, X. Z. Xiao et al. A new strategy to remarkably improve the low-temperature reversible hydrogen desorption performances of LiBH4 by compositing with fluorographene. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017; 42: 20046-20055.
[95] L. T. Zhang, J. G. Zheng, X. Z. Xiao et al. Enhanced hydrogen storage properties of a dualcation (Li+, Mg2+) borohydride and its dehydrogenation mechanism. Rsc Advances 2017; 7: 36852-36859.
[94] L. T. Zhang, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, J. G. Zheng, X. Huang. Enhanced hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 with numerous hydrogen diffusion channels provided by Na2Ti3O7 nanotubes. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2017; 5: 6178-6185.
[93] X. Z. Xiao, T. Qin, Y. Jiang et al. Significantly enhanced hydrogen desorption properties of Mg(AlH4)2 nanoparticles synthesized using solvent free strategy. Progress In Natural Science-Materials International 2017; 27: 112-120.
[92] C. C. Weng, X. Z. Xiao, X. Huang et al. Effect of Mn substitution for Co on the structural, kinetic, and thermodynamic characteristics of ZrCo1-xMnx (x=0-0.1) alloys for tritium storage. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017; 42: 28498-28506.
[91] J. Sun, X. Z. Xiao, Z. J. Zheng et al. Synthesis of nanoscale CeAl4 and its high catalytic efficiency for hydrogen storage of sodium alanate. Rare Metals 2017; 36: 77-85.
[90] M. Li, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, X. Huang, Y. J. Liu, L. X. Chen. Carbon coated sodium-titanate nanotube as an advanced intercalation anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Alloys And Compounds 2017; 712: 365-372.
[89] M. Li, X. Xiao, Y. Liu, W. Zhang, Y. Zhang, L. Chen. Ternary perovskite cobalt titanate/graphene composite material as long-term cyclic anode for lithium-ion battery. Journal of Alloys And Compounds 2017; 700: 54-60.
[88] Y. Q. Jiang, X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao et al. La2O3-modified highly dispersed AuPd alloy nanoparticles and their superior catalysis on the dehydrogenation of formic acid. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017; 42: 9353-9360.
[87] X. Huang, X. Z. Xiao, W. Zhang et al. Transition metal (Co, Ni) nanoparticles wrapped with carbon and their superior catalytic activities for the reversible hydrogen storage of magnesium hydride. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017; 19: 4019-4029.
[86] B. Zhai, X. Xiao, W. Lin, X. Huang, X. Fan, S. Li, H. Ge, Q. Wang, and L. Chen. Enhanced hydrogen desorption properties of LiBH4-Ca(BH4)2 by a synergetic effect of nanoconfinement and catalysis, Int. J Hydrogen Energ, 2016, 41(39), 17462-17470.
[85] C. C. Xu, X. Z. Xiao, J. Shao, L. X. Liu, T. Qin, and L. X. Chen. Effects of Ti-based additives on Mg2FeH6 dehydrogenation properties, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(3), 791-798.
[84] X. Z. Xiao, Z. Liu, S. Saremi-Yarahmadi, and D. H. Gregory: 'Facile preparation of beta-/gamma-MgH2 nanocomposites under mild conditions and pathways to rapid dehydrogenation, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(15), 10492-10498.
[83] G. Tu, J. He, X. Xiao, L. Chen, Q. Ren, X. Du, and M. Luo: 'Synergetic Effect of NbH@h-BN on Dehydrogenation of LiBH4, Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities-Chinese, 2016, 37(10), 1757-1762.
[82] M. Li, X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, X. Huang, Y. Q. Jiang, and L. X. Chen. Ternary perovskite nickel titanate/reduced graphene oxide nano-composite with improved lithium storage properties, Rsc Advances, 2016, 6(66), 61312-61318.
[81] Y. Q. Jiang, X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, T. Qin, L. T. Zhang, F. L. Jiang, M. Li, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, and L. X. Chen. Novel AgPd hollow spheres anchored on graphene as an efficient catalyst for dehydrogenation of formic acid at room temperature, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(2), 657-666.
[80] X. Huang, X. Z. Xiao, J. Shao, B. Zhai, X. L. Fan, C. J. Cheng, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, and L. X. Chen. Building robust architectures of carbon-wrapped transition metal nanoparticles for high catalytic enhancement of the 2LiBH4-MgH2 system for hydrogen storage cycling performance, Nanoscale, 2016, 8(31), 14898-14908.
[79]Guoping Tu, Xuezhang Xiao, Yiqun Jiang, Teng Qin, Shouquan Li, Hongwei Ge, Qidong Wang and Lixin Chen. Composite Cooperative enhancement on the hydrogen desorption kinetics of LiBH4 by co-doping with NbCl5 and hexagonal BN, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015; 40, 10527–10535.
[78]Guoping Tu, Xuezhang Xiao, Teng Qin, Yiqun Jiang, Shouquan Li, Hongwei Ge, Qidong Wang and Lixin Chen. Significantly improved de/rehydrogenation properties of lithium borohydride modified with hexagonal boron nitride, RSC Advances, 2015; 5, 51110–51115.
[77]Jie Shao, Xuezhang Xiao, Xiulin Fan, Xu Huang, Bing Zhai, Shouquan Li, Hongwei Ge, Qidong Wang, Lixin Chen. Enhanced hydrogen storage capacity and reversibility of LiBH4 nanoconfined in the densified zeolite-templated carbon with high mechanical stability, Nano Energy, 2015; 15, 244−255.
[76]C. C. Xu, X. Z. Xiao, J. Shao, L. T. Zhang, T. Qin, L. X. Chen. Effects of Ti-based additives on the Mg2FeH6 dehydrogenation properties, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015; in press.
[75]Liuting Zhang, Xuezhang Xiao, Chenchen Xu, Jiaguang Zheng, Xiulin Fan, Jie Shao, Shouquan Li, Hongwei Ge, Qidong Wang, Lixin Chen. Remarkably Improved Hydrogen Storage Performance of MgH2 Catalyzed by Multi-valence NbHx Nanoparticles, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015; 119, 8554−8562.
[74]Langxia Liu, Lixin Chen, Xuezhang Xiao, Chenchen Xu, Jian Sun, Shouquan Li, Hongwei Ge, Lijun Jiang. Influence of annealing treatment on the microstructure and hydrogen storage performance of Ti1.02Cr1.1Mn0.3Fe0.6 alloy for hybrid hydrogen storage application. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015; 636: 117-123.
[73]X. Z. Xiao, C. C. Xu, J. Shao, L. T. Zhang, T. Qin, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Remarkable Hydrogen Desorption Properties and Mechanisms for Mg2FeH6@MgH2 Core-Shell Nanostructure, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015; 3: 5517-5524.
[72]L. T. Zhang, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Fast hydrogen release under moderate conditions from NaBH4 destabilized by fluorographite, RSC Advances, 2014; 4: 2550-2556.
[71]L. T. Zhang, L. X. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, J. Shao, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Fluorographene nanosheets enhanced hydrogen absorption and desorption performances of magnesium hydride, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014; 39: 12715-12726.
[70]L. T. Zhang, L. X. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, Z. W. Chen, S. K. Wang, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Superior dehydrogenation performance of nanoscale lithium borohydride modified with fluorographite, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014; 39: 896-904.
[69]Xiulin Fan, JieShao, XuezhangXiao, XinhuaWang, Shouquan Li, HongweiGe, LixinChen. SnLi4.4 nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon matrix as high performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries, Nano Energy, 2014; 9, 196−203.
[68]X. Z. Xiao, S. K. Wang, G. P. Tu, L. T. Zhang, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Enhanced reversible hydrogen storage performance of NbCl5 doped 2LiH-MgB2 composite, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014; 39: 2132-2141.
[67]X. Z. Xiao, S. K. Wang, X. L. Fan, C. C. Xu, J. Sun, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Improved de/hydrogenation properties and favorable reaction mechanism of CeH2 + KH co-doped sodium aluminum hydride, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014; 39: 6577-6587.
[66]J. Shao, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, L. T. Zhang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Low-Temperature Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties of LiBH4: A Synergetic Effect of Nanoconfinement and Nanocatalysis, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014; 118: 11252-11260.
[65]L. Y. Han, X. Z. Xiao, S. K. Wang, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, L. X. Chen. Dehydrogenation Behavior and Mechanism of LiBH4 Doped with Ce2Mg17 and Its Hydride, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014; 43: 1935-1938.
[64]L. Y. Han, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, Y. Li, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Enhanced dehydrogenation performances and mechanism of LiBH4/Mg17Al12-hydride composite, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014; 24: 152-157.
[63]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, J. Shao, L. T. Zhang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Superior Catalytic Effects of Transition Metal Boride Nanoparticles on the Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties of Li-Mg-B-H System, Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2014; 31: 195-200.
[62]X. L. Fan, J. Shao, X. Z. Xiao, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, L. X. Chen, C. S. Wang. In situ synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles encapsulated in micro/mesoporous carbon foam as a high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014; 2: 18367-18374.
[61]X. L. Fan, J. Shao, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge. Carbon encapsulated 3D hierarchical Fe3O4 spheres as advanced anode materials with long cycle lifetimes for lithium-ion batteries, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014; 2: 14641-14648.
[60]Z. W. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, L. X. Liu, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Influence of Ti super-stoichiometry on the hydrogen storage properties of Ti1+xCr1.2Mn0.2Fe0.6 (x=0-0.1) alloys for hybrid hydrogen storage application, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014; 585: 307-311.
[59]X. Z. Xiao, L. T. Zhang, X. L. Fan, L. Y. Han, J. Shao, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Synergetic Effect of in Situ Formed Nano NbH and LiH1-xFx for Improving Reversible Hydrogen Storage Properties of the Li-Mg-B-H System, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013; 117: 12019-12025.
[58]Z. Wu, L. X. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang. Influence of lanthanon hydride catalysts on hydrogen storage properties of sodium alanates, Journal of Rare Earths, 2013; 31: 502-506.
[57]S. K. Wang, Z. J. Li, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, Z. W. Chen, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, L. X. Chen. Influence of KH on Reversible Dehydriding Performance of Na-Al-H Complex Hydride, Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2013; 29: 1804-1808.
[56]J. Shao, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, L. Y. Han, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Enhanced hydriding-dehydriding performance of a 2LiH-MgB2 composite by the catalytic effects of Ni-B nanoparticles, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013; 1: 10184-10192.
[55]J. Shao, X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, L. X. Chen, H. Y. Zhu, S. Q. Yu, Z. D. Gong, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. A low temperature mechanochemical synthesis and characterization of amorphous Ni-B ultrafine nanoparticles, Mater. Lett., 2013; 109: 203-206.
[54]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, J. Shao, L. T. Zhang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Size effect on hydrogen storage properties of NaAlH4 confined in uniform porous carbons, Nano Energy, 2013; 2: 995-1003.
[53]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, L. T. Zhang, J. Shao, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Significantly improved hydrogen storage properties of NaAlH4 catalyzed by Ce-based nanoparticles, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013; 1: 9752-9759.
[52]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. High catalytic efficiency of amorphous TiB2 and NbB2 nanoparticles for hydrogen storage using the 2LiBH4-MgH2 system, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013; 1: 11368-11375.
[51]Z. W. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, L. X. Liu, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Development of Ti-Cr-Mn-Fe based alloys with high hydrogen desorption pressures for hybrid hydrogen storage vessel application, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013; 38: 12803-12810.
[50]X. Z. Xiao, J. Shao, L. X. Chen, H. Q. Kou, X. L. Fan, S. S. Deng, L. T. Zhang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Effects of NbF5 addition on the de/rehydrogenation properties of 2LiBH4/MgH2 hydrogen storage system, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012; 37: 13147-13154.
[49]J. Shao, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Enhanced hydriding-dehydriding performance of 2LiBH4-MgH2 composite by the catalytic effects of transition metal chlorides, Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012; 22: 20764-20772.
[48]Y. Li, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, L. Y. Han, J. Shao, X. L. Fan, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang. Effects of Fluoride Additives on the Hydrogen Storage Performance of 2LiBH4-Li3AlH6 Destabilized System, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012; 116: 22226-22230.
[47]C. X. Li, X. Z. Xiao, P. Q. Ge, J. W. Xue, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, L. X. Chen. Investigation on synthesis, structure and catalytic modification of Ca(AlH4)2 complex hydride, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012; 37: 936-941.
[46]H. Q. Kou, X. Z. Xiao, J. X. Li, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Effects of fluoride additives on dehydrogenation behaviors of 2LiBH4+MgH2 system, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012; 37: 1021-1026.
[45]K. Jiang, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, L. Y. Han, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. A comparative study of the hydrogen storage properties of LiBH4 doping with CaHCl and CaH2, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012; 539: 103-107.
[44]Z. M. Hang, X. Z. Xiao, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, C. P. Chen, L. X. Chen. Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti10V77Cr6Fe6Zr alloy, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012; 529: 128-133.
[43]S. S. Deng, X. Z. Xiao, L. Y. Han, Y. Li, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Hydrogen storage performance of 5LiBH4+Mg2FeH6 composite system, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012; 37: 6733-6740.
[42]S. S. Deng, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, L. Y. Han, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Effects of Stoichiometry and Dehydrogenation Back-pressure on the Dehydrogenation Behavior of LiBH4+xMg2NiH4 Composites, Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities-Chinese, 2012; 33: 2030-2034.
[41]X. Z. Xiao, K. R. Yu, X. L. Fan, Z. Wu, X. H. Wang, C. P. Chen, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Synthesis and hydriding/dehydriding properties of nanosized sodium alanates prepared by reactive ball-milling, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011; 36: 539-548.
[40]X. Z. Xiao, C. X. Li, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, H. Q. Kou, Q. D. Wang. Synthesis and dehydrogenation of CeAl4-doped calcium alanate, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011; 509: S743-S746.
[39]S. K. Peng, X. Z. Xiao, Z. M. Hang, F. Wu, C. X. Li, S. Q. Li, L. X. Chen. Phase-structure and Hydrogen Storage Behaviors of Mg+10% Ni2P Composite Prepared by Reactive Ball-Milling, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2011; 40: 1387-1391.
[38]C. X. Li, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, K. Jiang, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang. Synthesis of calcium alanate and its dehydriding performance enhanced by FeF3 doping, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011; 509: 590-595.
[37]H. Q. Kou, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang. Formation mechanism of MgB2 in 2LiBH4 + MgH2 system for reversible hydrogen storage, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011; 21: 1040-1046.
[36]K. Jiang, X. Z. Xiao, S. S. Deng, M. Zhang, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, L. X. Chen. A Novel Li-Ca-B-H Complex Borohydride: Its Synthesis and Hydrogen Storage Properties, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011; 115: 19986-19993.
[35]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang. Investigation on the nature of active species in the CeCl3-doped sodium alanate system, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011; 509: S750-S753.
[34]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Enhanced Hydriding-Dehydriding Performance of CeAl2-Doped NaAlH4 and the Evolvement of Ce-Containing Species in the Cycling, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011; 115: 2537-2543.
[33]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Direct synthesis and hydrogen storage behaviors of nanocrystalline Na2LiAlH6, Journal of Materials Science, 2011; 46: 3314-3318.
[32]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, L. Y. Han, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Hydriding-dehydriding kinetics and the microstructure of La- and Sm-doped NaAlH4 prepared via direct synthesis method, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011; 36: 10861-10869.
[31]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, L. Y. Han, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, Q. D. Wang. Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Modeling Investigation on the Dehydrogenation of CeAl4-Doped NaAlH4 Hydrogen Storage Material, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011; 115: 22680-22687.
[30]L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, J. W. Xue, S. Q. Li, H. W. Ge, C. P. Chen. Influence of TiC catalyst on absorption/desorption behaviors and microstructures of sodium aluminum hydride, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011; 21: 1297-1302.
[29]X. Z. Xiao, G. C. Liu, S. K. Peng, K. R. Yu, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, L. X. Chen. Microstructure and hydrogen storage characteristics of nanocrystalline Mg plus x wt% LaMg2Ni (x=0-30) composites, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010; 35: 2786-2790.
[28]S. K. Peng, X. Z. Xiao, R. J. Xu, L. Li, F. Wu, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Hydrogen storage behaviors and microstructure of MF3 (M=Ti, Fe)-doped magnesium hydride, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010; 20: 1879-1884.
[27]Z. M. Hang, X. Z. Xiao, K. R. Yu, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, L. X. Chen. Influence of Fe content on the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti16Zr5Cr22V57-xFex (x=2-8) alloys, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010; 35: 8143-8148.
[26]Z. M. Hang, X. Z. Xiao, D. Z. Tan, Z. H. He, W. P. Li, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, L. X. Chen. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti10V84-xFe6Zrx (x=1-8) alloys, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010; 35: 3080-3086.
[25]Z. M. Hang, L. X. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, Y. Q. Lei, Q. D. Wang. The effect of Cr content on the structural and hydrogen storage characteristics of Ti10V80-xFe6Zr4Crx (x=0-14) alloys, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010; 493: 396-400.
[24]X. Z. Xiao, X. L. Fan, K. R. Yu, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, Q. D. Wang, L. X. Chen. Catalytic Mechanism of New TiC-Doped Sodium Alanate for Hydrogen Storage, Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009; 113: 20745-20751.
[23]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, Z. M. Hang, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, Y. Q. Lei, Q. D. Wang. Microstructures and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of novel Mg-Al-Ni amorphous composites, Electrochemistry Communications, 2009; 11: 515-518.
[22]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, X. H. Wang, C. P. Chen, Y. Q. Lei, Q. D. Wang. Direct synthesis of nanocrystalline NaAlH4 complex hydride for hydrogen storage, Applied Physics Letters, 2009; 94.
[21]Y. M. Jia, F. Y. Liu, X. Z. Xiao, Z. M. Hang, Y. Q. Lei, L. X. Chen. Microstructure and Electrochemical Properties of V2.1TiNi0.4Zr0.06Cu0.03M0.10 (M=Cr, Co, Fe, Nb, Ta) Hydrogen Storage Alloys, Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2009; 25: 247-252.
[20]Y. M. Jia, L. X. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, K. R. Yu, T. Ying, Y. Q. Lei. Effect of quenching treatment on the phase structure and electrochemical properties of V2.1TiNi0.4Zr0.06Mn0.05 alloy, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009; 34: 7756-7760.
[19]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, J. C. Hou, Z. Zhang, Y. B. Liu, Z. Wu, C. P. Chen, Q. D. Wang, L. Chen. Reversible hydrogen storage behaviors and microstructure of TiC-doped sodium aluminum hydride, Journal of Materials Science, 2009; 44: 4700-4704.
[18]X. L. Fan, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, K. R. Yu, Z. Wu, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang. Active species of CeAl4 in the CeCl3-doped sodium aluminium hydride and its enhancement on reversible hydrogen storage performance, Chemical Communications, 2009: 6857-6859.
[17]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, Q. D. Wang. Reversible hydrogen storage properties and favorable co-doping mechanism of the metallic Ti and Zr co-doped sodium aluminum hydride, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008; 33: 64-73.
[16]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. L. Fan, H. W. Ge, S. Q. Li, T. Ying, X. H. Wang, C. P. Chen. Influence of Ti-Zr catalysts on reversible hydrogen storage characteristics of NaH/Al composite, Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2008; 24: 423-427.
[15]X. Z. Xiao, X. H. Wang, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, Y. Tang, C. P. Chen. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of La1.8Ca0.2Mg14Ni3 + x% Ti composites, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007; 36: 790-793.
[14]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, Q. D. Wang, C. P. Chen. The hydrogen storage properties and microstructure of Ti-doped sodium aluminum hydride prepared by ball-milling, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007; 32: 2475-2479.
[13]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, Q. D. Wang, C. P. Chen. Influence of temperature and hydrogen pressure on the hydriding/dehydriding behavior of Ti-doped sodium aluminum hydride, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007; 32: 3954-3958.
[12]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, Z. M. Hang, C. P. Chen, Q. D. Wang. Dehydriding properties of Ti or/and Zr-doped sodium aluminum hydride prepared by ball-milling, Physica Scripta, 2007; T129: 95-98.
[11]X. Z. Xiao, X. H. Wang, L. H. Gao, L. Wang, C. P. Chen. Electrochemical properties of amorphous Mg-Fe alloys mixed with Ni prepared by ball-milling, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006; 413: 312-318.
[10]X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen. Preparation and hydrogen storage characteristics of Ti-NaAlH4 complex hydride, Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2006; 22: 1511-1515.
[9]X. Z. Xiao, C. P. Chen, X. H. Wang, L. X. Chen. Mechanical ball milling preparation and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of amorphous Mg-Fe composites, Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities-Chinese, 2006; 27: 116-120.
[8]X. H. Wang, X. Z. Xiao, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti-doped NaH/Al composites prepared by ball-milling, Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities-Chinese, 2006; 27: 1360-1362.
[7]L. Wang, X. H. Wang, L. X. Chen, C. P. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, L. H. Gao, Q. D. Wang. Electrode properties of La2Mg17 alloy ball-milled with xwt.% cobalt powder (x=50, 100, 150 and 200), Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006; 414: 248-252.
[6]L. Wang, X. H. Wang, L. X. Chen, C. P. Chen, X. Z. Xiao, L. H. Gao, Q. D. Wang. Effects of ball-milling time and Bi2O3 addition on electrochemical performance of ball-milled La2Mg17+200 wt.% Ni composites, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006; 416: 194-198.
[5]Y. Tang, X. H. Wang, X. Z. Xiao, S. L. Du, Y. Q. Lei. Microstructure and electrochemical properties of amorphous composites of ball-milled Mg2Ni0.95Sn0.05 + x wt% Ni, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006; 35: 1303-1307.
[4]S. L. Du, X. H. Wang, L. X. Chen, S. Q. Li, C. P. Chen, Y. Tang, X. Z. Xiao. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti1.0VxMn2-x(x=0.6 to 1.6) alloys, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006; 35: 1285-1288.
[3] X. Z. Xiao, C. P. Chen, X. H. Wang, L. X. Chen, L. Wang, L. H. Gao. Microstructure and electrochemical properties of amorphous Mg-Fe-Ni hydrogen storage electrode material, Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2005; 21: 565-568.
[2]L. Wang, X. H. Wang, C. P. Chen, X. Z. Xiao. Electrochemical properties of CeMg12+x%Ni composites (x=0 similar to 200) prepared by ball-milling, Journal of Rare Earths, 2005; 23: 382-385.
[1]L. H. Gao, C. P. Chen, L. X. Chen, X. H. Wang, J. W. Zhang, X. Z. Xiao, Q. D. Wang. Hydriding/dehydriding behaviors of La1.8Ca0.2Mg14Ni3 alloy modified by mechanical ball-milling under argon, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005; 399: 178-182.
Hydrogen Storage Materials Research Group